EV Charging Basics
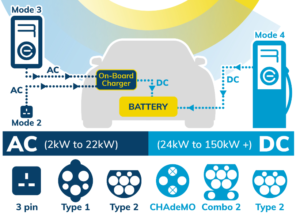
EV charging points are primarily defined by the power (in kW) they can produce and therefore what speed they are capable of charging an EV. While connector types are also a key issue, most EVs are equipped with two or more cables to allow the use of chargers with different connector outlets.
 Target Applications for EV and PHEV
Target Applications for EV and PHEV
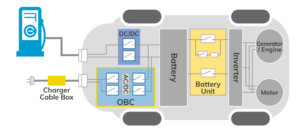
The OBC function can either be a standalone module or integrated with the main HV DC-DC. Its function is to take AC power provided via the vehicle charging port and recharge the vehicle battery.
On-Board Chargers
At the heart of any electric (EV) or plug-in hybrid (PHEV) vehicle lays the high-voltage (200 to 450 VDC) battery and its associated charging system. The on-board charger (OBC) provides the means to recharge the battery from the AC mains either at home or from outlets found in private or public charging stations. From a 3.6 kW single-phase to a 22 kW three-phase high-power converter, today’s (OBCs) On-Board Chargers must have the highest possible efficiency and reliability to ensure rapid charging times as well as meet the limited space and weight requirements
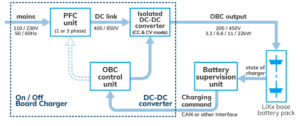
Level 1 and Level 2 Charging the On-Board Charger (OBC)
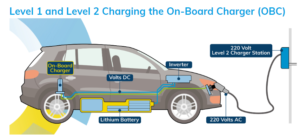
In both Level 1 and Level 2 charging the onboard charger converts AC current into DC current and steps up the voltage to the level needed to efficiently charge the batteries.








